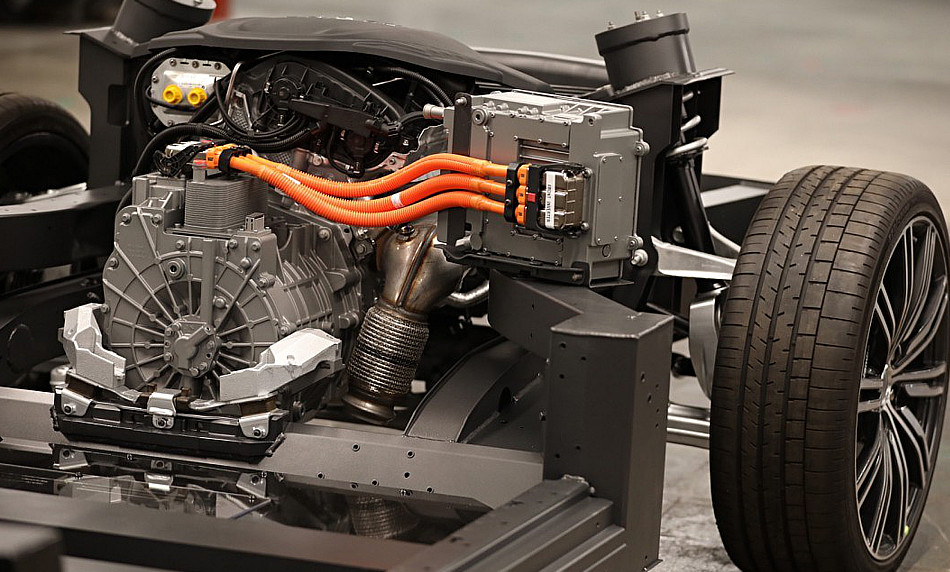
The Yangwang U8 is a 3.5-tonne premium SUV from China, featuring a 45 kWh battery supplemented by a range extender. In this case, the range extender is an internal combustion engine used exclusively to charge the battery, functioning purely as a gasoline-powered generator. This engine has no driveshaft and is not connected to the wheels; the U8’s propulsion is provided entirely by its electric motors.
The U8’s legacy gasoline engine provides charging on the move, supported by a 75-liter fuel tank that enables a total range of 620 miles. This raises the question: How can Yangwang claim to be sustainable and environmentally friendly when the U8 employs two opposing technologies, one being a legacy technology and the other being seen as the future?
Is the range extender an obsolete technology, or is it a transitional solution until battery technology fully surpasses the internal combustion engine?
A range extender engine differs from a typical 4-cylinder engine, with pistons mounted horizontally and the entire unit being significantly more compact. However, integrating two opposing power plants adds to the vehicle’s complexity. Mercedes-Benz experimented with range extenders but ultimately abandoned the idea after engineering tests revealed it was prohibitively expensive.
Despite this, Yangwang concluded that the U8 would benefit from incorporating a range extender to reduce battery size and overall weight. Nonetheless, the vehicle still weighs over 3.5 tonnes, which is more than 400 kg heavier than the Tesla Cybertruck.